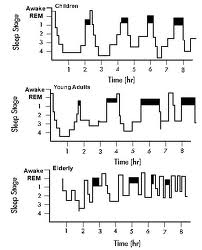
In order to understand why we need adequate sleep, we need to have a better understanding of the sleep cycle. Scientists, Doctors, and Psychologists study sleep and sleep patterns using a machine known as the Electrocardiogram (EEG). The EEG has identified 5 stages of sleep.
Stage 1: This stage of sleep initiates the drowsiness effect, which causes a person to drift in and out of sleep.
Stage 2: In this stage, eye movement diminishes. An EEG reveals slower and more rapid brain wave patterns.
Stage 3: Delta waves are seen with an EEG. These delta waves are small and fast waves.
Stage 4: Delta waves dominate this stage of sleep.Stage 5 or REM: At this time, REM (rapid eye movement) occurs. Physiologically, the individual has more rapid breathing, eye jerks, increased heart rate, and increased blood pressure. Dreams, bed wetting and sleepwalking also may occur at this stage.
Now that we have a better understanding of sleep patterns, the stages of sleep, and how the brain reacts during sleep, let's discuss the prerequisites for achieving better sleep.
2) Take a warm bath. A warm bath cleanses and creates a soothing effect for the body. Lavender can also be added to bath water to produce a more soothing effect.
3) Clean sheets. Clean sheets create are more relaxing for the body, so sometimes changing the sheets is beneficial.
4) Decreased Activity. Only use the bed to sleep. Do not use the bed for reading, watching television, eating, etc. In other words, obeying this guideline will help your body to naturally recognise that when you do go to bed you are actually going to sleep.
5) Listening to Music or Water. Some music and the sound of water, such as waterfall, rainfall, or the sound of an ocean can create a more relaxing environment.
6) Activity. If you wake up in the middle of sleeping, get out of bed and move around. Do chores around the house, get a glass of milk, etc. This will decrease energy to where you feel more drowsy. Staying in bed will only cause you to dwell on not getting sleep.
7) Exercise. Although it's important to get out of bed if insomnia is an issue, do not exercise before going to sleep. Exercise increase endorphins. These endorphins produce an energizing effect that detour you from sleeping.
8) Noise. If noise is an issue, turn on a fan. A fan will block out most of the noise.
9) Room temperature. If you are unable to sleep because of the room temperature, change the thermostat to a more relaxing temperature.
10) Medication. If insomnia persists, speak to your Primary Care Physician (PCP) and ask for a sedative, such as melatonin, Trezadone, Ambien, etc. According to majority of my patients who have insomnia, Trazadone is an effective sleep medication.
Although, some of these guidelines may not be sufficient for some individuals, everyone needs to determine the most effective ways to get adequate sleep. Adequate sleep is beneficial because a substantial amount of sleep reduces illnesses, increases frontal lobe activity, and increases our longevity. It is also extremely important to understand our body's anatomy and physiology and how the sleep stages benefit sleep. Overall, adults spend 50% of their time in stage 2 sleep, 20% in REM sleep, and 30% in the other stages of sleep. As we get older, we spend less time in REM sleep. Since the elderly do not get adequate REM sleep, they feel more lethargic. This explains why the elderly need to take more naps during the day. Therefore, sleep, it does the body good.